A schema is a collection of database objects, including tables, views, indexes, and synonyms. You can arrange schema objects in the schema models designed for data warehousing in a variety of ways.
Star Schema :
The star schema (also called star-join schema, data cube, or multi-dimensional schema) is the simplest style of data warehouse schema. The star schema consists of one or more fact tables referencing any number of dimension tables
Star Schemas Architecture Example :

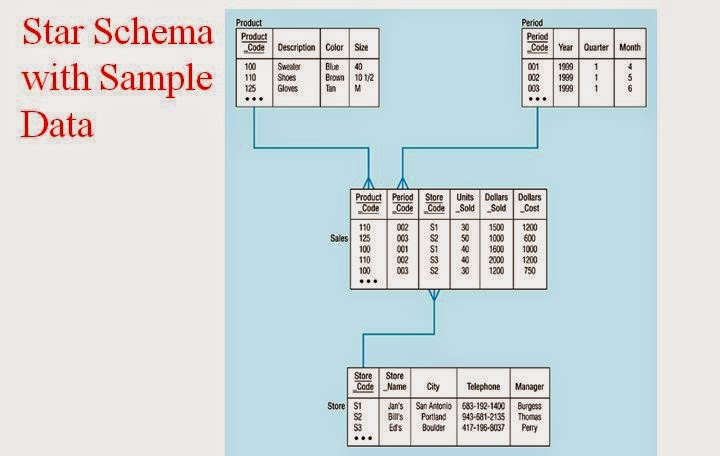
Star Schemas Architecture Example with data :
The facts that the data warehouse helps analyze are classified along different dimensions:
Dimension tables have a simple primary key, while fact tables have a set of foreign keys which make up a compound primary key consisting of a combination of relevant dimension keys.
Advantages :
Star Schema :
The star schema (also called star-join schema, data cube, or multi-dimensional schema) is the simplest style of data warehouse schema. The star schema consists of one or more fact tables referencing any number of dimension tables
Star Schemas Architecture Example :
Star Schemas Architecture Example with data :
The facts that the data warehouse helps analyze are classified along different dimensions:
- The fact table holds the main data. It includes a large amount of aggregated data, such as price and units sold. There may be multiple fact tables in a star schema.
- Dimension tables, which are usually smaller than fact tables, include the attributes that describe the facts. Often this is a separate table for each dimension. Dimension tables can be joined to the fact table(s) as needed.
Dimension tables have a simple primary key, while fact tables have a set of foreign keys which make up a compound primary key consisting of a combination of relevant dimension keys.
Advantages :
- Provide a direct and intuitive mapping between the business entities being analyzed by end users and the schema design.
- Provide highly optimized performance for typical star queries.
- Are widely supported by a large number of business intelligence tools, which may anticipate or even require that the data-warehouse schema contain dimension tables

No comments:
Post a Comment